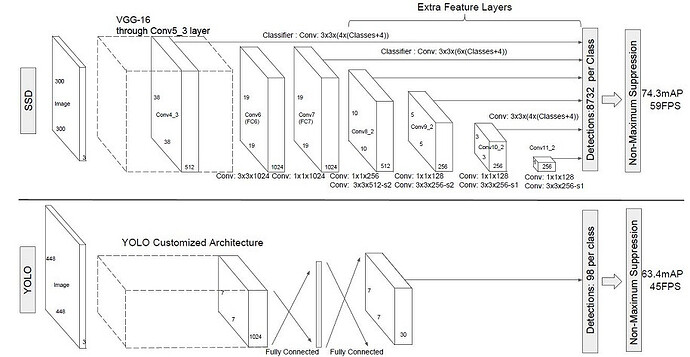
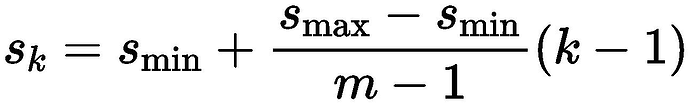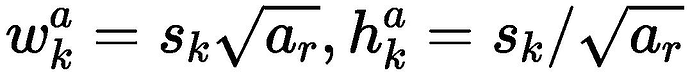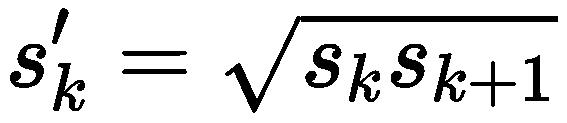SSD,全称Single Shot MultiBox Detector,是Wei Liu在ECCV 2016上提出的一种目标检测算法。使用Nvidia Titan X在VOC 2007测试集上,SSD对于输入尺寸300x300的网络,达到74.3%mAP以及59FPS;对于512x512的网络,达到了76.9%mAP ,超越当时最强的Faster RCNN(73.2%mAP)。具体可参考论文。 SSD目标检测主流算法分成可以两个类型:
- two-stage方法:RCNN系列
通过算法产生候选框,然后再对这些候选框进行分类和回归。- one-stage方法:yolo和SSD
直接通过主干网络给出类别位置信息,不需要区域生成。
模型结构
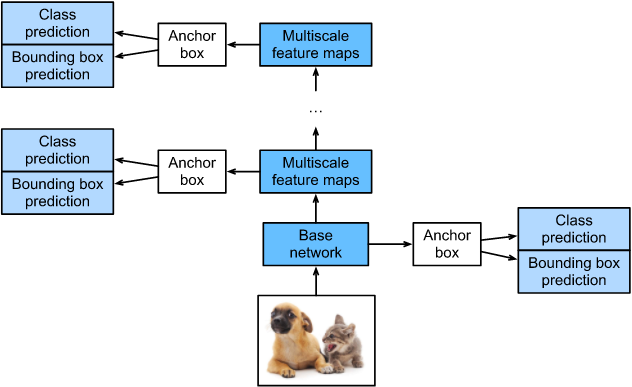
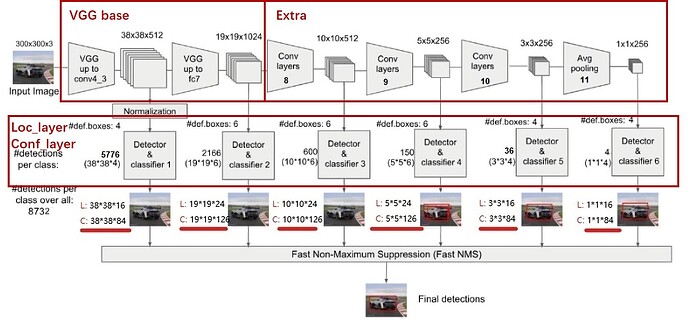
SSD采用VGG16作为基础模型,然后在VGG16的基础上新增了卷积层来获得更多的特征图以用于检测。SSD的网络结构如图所示。上面是SSD模型,下面是Yolo模型,可以明显看到SSD利用了多尺度的特征图做检测。
1 环境准备
1.进入ModelArts官网
云平台帮助用户快速创建和部署模型,管理全周期AI工作流,选择下面的云平台以开始使用昇思MindSpore,可以在昇思教程中进入ModelArts官网
创建notebook,点击【打开】启动,进入ModelArts调试环境页面。
注意选择西南-贵阳一,mindspore_2.3.0
等待环境搭建完成
下载案例notebook文件
基于MindSpore框架的SSD案例实现:https://github.com/kkyi10/SSDNet_ms/blob/master/ssd.ipynb
选择ModelArts Upload Files上传.ipynb文件
进入昇思MindSpore官网,点击上方的安装获取安装命令
MindSpore版本升级,镜像自带的MindSpore版本为2.3,该活动要求在MindSpore2.4.0版本体验,所以需要进行MindSpore版本升级。
命令如下:
export no_proxy='a.test.com,127.0.0.1,2.2.2.2'
pip install https://ms-release.obs.cn-north-4.myhuaweicloud.com/2.4.0/MindSpore/unified/aarch64/mindspore-2.4.0-cp39-cp39-linux_aarch64.whl --trusted-host ms-release.obs.cn-north-4.myhuaweicloud.com -i https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple
回到Notebook中,在第一块代码前加命令
pip install --upgrade pip
pip install mindvision
pip install download
2 案例实现
2.1 环境准备与数据读取
本案例基于MindSpore-GPU 1.8.1版本实现,在GPU上完成模型训练。
案例所使用的数据为coco2017,数据集包含训练集、验证集以及对应的json文件,目录结构如下:
└─tiny_coco2017
├─annotations
├─instance_train2017.json
└─instance_val2017.json
├─val2017
└─train2017
为了更加方便地保存和加载数据,本案例中在数据读取前首先将coco数据集转换成MindRecord格式:MindRecord_COCO
MindRecord目录结构如下:
└─MindRecord_COCO
├─ssd.mindrecord0
├─ssd.mindrecord0.db
├─ssd_eval.mindrecord0
├─ssd_eval.mindrecord0.db
-
mindspore.mindrecord模块中定义了一个专门的类FileWriter可以将用户定义的原始数据写入MindRecord文件。
-
通过MindDataset接口,可以实现MindSpore Record文件的读取。
-
使用MindRecord的目标是归一化提供训练测试所用的数据集,并通过dataset模块的相关方法进行数据的读取,将这些高效的数据投入训练。
使用MindSpore Record数据格式可以减少磁盘IO、网络IO开销,从而获得更好的使用体验和性能提升。
import os
import numpy as np
from mindspore.mindrecord import FileWriter
from src.config import get_config
config = get_config()
def create_coco_label(is_training):
"""Get image path and annotation from COCO."""
from pycocotools.coco import COCO
#coco_root = os.path.join(config.data_path, config.coco_root)
coco_root = config.data_path
data_type = config.val_data_type
if is_training:
data_type = config.train_data_type
# Classes need to train or test.
train_cls = config.classes
train_cls_dict = {}
for i, cls in enumerate(train_cls):
train_cls_dict[cls] = i
anno_json = os.path.join(coco_root, config.instances_set.format(data_type))
coco = COCO(anno_json)
classs_dict = {}
cat_ids = coco.loadCats(coco.getCatIds())
for cat in cat_ids:
classs_dict[cat["id"]] = cat["name"]
image_ids = coco.getImgIds()
images = []
image_path_dict = {}
image_anno_dict = {}
for img_id in image_ids:
image_info = coco.loadImgs(img_id)
file_name = image_info[0]["file_name"]
anno_ids = coco.getAnnIds(imgIds=img_id, iscrowd=None)
anno = coco.loadAnns(anno_ids)
image_path = os.path.join(coco_root, data_type, file_name)
annos = []
iscrowd = False
for label in anno:
bbox = label["bbox"]
class_name = classs_dict[label["category_id"]]
iscrowd = iscrowd or label["iscrowd"]
if class_name in train_cls:
x_min, x_max = bbox[0], bbox[0] + bbox[2]
y_min, y_max = bbox[1], bbox[1] + bbox[3]
annos.append(list(map(round, [y_min, x_min, y_max, x_max])) + [train_cls_dict[class_name]])
if not is_training and iscrowd:
continue
if len(annos) >= 1:
images.append(img_id)
image_path_dict[img_id] = image_path
image_anno_dict[img_id] = np.array(annos)
return images, image_path_dict, image_anno_dict
def data_to_mindrecord_byte_image( is_training=True, prefix="ssd.mindrecord", file_num=8):
"""Create MindRecord file."""
mindrecord_path = os.path.join(config.data_path, config.mindrecord_dir, prefix)
writer = FileWriter(mindrecord_path, file_num)
images, image_path_dict, image_anno_dict = create_coco_label(is_training)
ssd_json = {
"img_id": {"type": "int32", "shape": [1]},
"image": {"type": "bytes"},
"annotation": {"type": "int32", "shape": [-1, 5]},
}
writer.add_schema(ssd_json, "ssd_json")
for img_id in images:
image_path = image_path_dict[img_id]
with open(image_path, 'rb') as f:
img = f.read()
annos = np.array(image_anno_dict[img_id], dtype=np.int32)
img_id = np.array([img_id], dtype=np.int32)
row = {"img_id": img_id, "image": img, "annotation": annos}
writer.write_raw_data([row])
writer.commit()
def create_mindrecord( prefix="ssd.mindrecord", is_training=True):
mindrecord_dir = os.path.join(config.data_path, config.mindrecord_dir)
mindrecord_file = os.path.join(mindrecord_dir, prefix + "0")
os.makedirs(mindrecord_dir,exist_ok=True)
if not os.path.exists(mindrecord_file):
print("Create {} Mindrecord.".format(prefix))
data_to_mindrecord_byte_image(is_training, prefix)
print("Create {} Mindrecord Done, at {}".format(prefix,mindrecord_dir))
else:
print(" {} Mindrecord exists.".format(prefix))
return mindrecord_file
# 数据转换为mindrecord格式
mindrecord_file = create_mindrecord("ssd.mindrecord", True)
eval_mindrecord_file = create_mindrecord("ssd_eval.mindrecord", False)
数据预处理
为了使模型对于各种输入对象大小和形状更加鲁棒,SSD算法每个训练图像通过以下选项之一随机采样 :
- 使用整个原始输入图像
- 采样一个区域,使采样区域和原始图片最小的交并比重叠为0.1,0.3,0.5,0.7或0.9。
- 随机采样一个区域
每个采样区域的大小为原始图像大小的[0.3,1] ,长宽比在1/2和2之间。如果真实标签框中心在采样区域内,则保留两者重叠部分作为新图片的真实标注框。在上述采样步骤之后,将每个采样区域大小调整为固定大小,并以0.5的概率水平翻转。
import cv2
def _rand(a=0., b=1.):
return np.random.rand() * (b - a) + a
def intersect(box_a, box_b):
"""Compute the intersect of two sets of boxes."""
max_yx = np.minimum(box_a[:, 2:4], box_b[2:4])
min_yx = np.maximum(box_a[:, :2], box_b[:2])
inter = np.clip((max_yx - min_yx), a_min=0, a_max=np.inf)
return inter[:, 0] * inter[:, 1]
def jaccard_numpy(box_a, box_b):
"""Compute the jaccard overlap of two sets of boxes."""
inter = intersect(box_a, box_b)
area_a = ((box_a[:, 2] - box_a[:, 0]) *
(box_a[:, 3] - box_a[:, 1]))
area_b = ((box_b[2] - box_b[0]) *
(box_b[3] - box_b[1]))
union = area_a + area_b - inter
return inter / union
# 随机裁剪图像和box
def random_sample_crop(image, boxes):
height, width, _ = image.shape
min_iou = np.random.choice([None, 0.1, 0.3, 0.5, 0.7, 0.9])
if min_iou is None:
return image, boxes
# max trails (50)
for _ in range(50):
image_t = image
w = _rand(0.3, 1.0) * width
h = _rand(0.3, 1.0) * height
# aspect ratio constraint b/t .5 & 2
if h / w < 0.5 or h / w > 2:
continue
left = _rand() * (width - w)
top = _rand() * (height - h)
rect = np.array([int(top), int(left), int(top + h), int(left + w)])
overlap = jaccard_numpy(boxes, rect)
# dropout some boxes
drop_mask = overlap > 0
if not drop_mask.any():
continue
if overlap[drop_mask].min() < min_iou and overlap[drop_mask].max() > (min_iou + 0.2):
continue
image_t = image_t[rect[0]:rect[2], rect[1]:rect[3], :]
centers = (boxes[:, :2] + boxes[:, 2:4]) / 2.0
m1 = (rect[0] < centers[:, 0]) * (rect[1] < centers[:, 1])
m2 = (rect[2] > centers[:, 0]) * (rect[3] > centers[:, 1])
# mask in that both m1 and m2 are true
mask = m1 * m2 * drop_mask
# have any valid boxes? try again if not
if not mask.any():
continue
# take only matching gt boxes
boxes_t = boxes[mask, :].copy()
boxes_t[:, :2] = np.maximum(boxes_t[:, :2], rect[:2])
boxes_t[:, :2] -= rect[:2]
boxes_t[:, 2:4] = np.minimum(boxes_t[:, 2:4], rect[2:4])
boxes_t[:, 2:4] -= rect[:2]
return image_t, boxes_t
return image, boxes
def ssd_bboxes_encode(boxes):
"""
Labels anchors with ground truth inputs.
Args:
boxex: ground truth with shape [N, 5], for each row, it stores [y, x, h, w, cls].
Returns:
gt_loc: location ground truth with shape [num_anchors, 4].
gt_label: class ground truth with shape [num_anchors, 1].
num_matched_boxes: number of positives in an image.
"""
def jaccard_with_anchors(bbox):
"""Compute jaccard score a box and the anchors."""
# Intersection bbox and volume.
ymin = np.maximum(y1, bbox[0])
xmin = np.maximum(x1, bbox[1])
ymax = np.minimum(y2, bbox[2])
xmax = np.minimum(x2, bbox[3])
w = np.maximum(xmax - xmin, 0.)
h = np.maximum(ymax - ymin, 0.)
# Volumes.
inter_vol = h * w
union_vol = vol_anchors + (bbox[2] - bbox[0]) * (bbox[3] - bbox[1]) - inter_vol
jaccard = inter_vol / union_vol
return np.squeeze(jaccard)
pre_scores = np.zeros((config.num_ssd_boxes), dtype=np.float32)
t_boxes = np.zeros((config.num_ssd_boxes, 4), dtype=np.float32)
t_label = np.zeros((config.num_ssd_boxes), dtype=np.int64)
for bbox in boxes:
label = int(bbox[4])
scores = jaccard_with_anchors(bbox)
idx = np.argmax(scores)
scores[idx] = 2.0
mask = (scores > matching_threshold)
mask = mask & (scores > pre_scores)
pre_scores = np.maximum(pre_scores, scores * mask)
t_label = mask * label + (1 - mask) * t_label
for i in range(4):
t_boxes[:, i] = mask * bbox[i] + (1 - mask) * t_boxes[:, i]
index = np.nonzero(t_label)
# Transform to tlbr.
bboxes = np.zeros((config.num_ssd_boxes, 4), dtype=np.float32)
bboxes[:, [0, 1]] = (t_boxes[:, [0, 1]] + t_boxes[:, [2, 3]]) / 2
bboxes[:, [2, 3]] = t_boxes[:, [2, 3]] - t_boxes[:, [0, 1]]
# Encode features.
bboxes_t = bboxes[index]
default_boxes_t = default_boxes[index]
bboxes_t[:, :2] = (bboxes_t[:, :2] - default_boxes_t[:, :2]) / (default_boxes_t[:, 2:] * config.prior_scaling[0])
tmp = np.maximum(bboxes_t[:, 2:4] / default_boxes_t[:, 2:4], 0.000001)
bboxes_t[:, 2:4] = np.log(tmp) / config.prior_scaling[1]
bboxes[index] = bboxes_t
num_match = np.array([len(np.nonzero(t_label)[0])], dtype=np.int32)
return bboxes, t_label.astype(np.int32), num_match
def preprocess_fn(img_id, image, box, is_training):
"""Preprocess function for dataset."""
cv2.setNumThreads(2)
def _infer_data(image, input_shape):
img_h, img_w, _ = image.shape
input_h, input_w = input_shape
image = cv2.resize(image, (input_w, input_h))
# When the channels of image is 1
if len(image.shape) == 2:
image = np.expand_dims(image, axis=-1)
image = np.concatenate([image, image, image], axis=-1)
return img_id, image, np.array((img_h, img_w), np.float32)
def _data_aug(image, box, is_training, image_size=(300, 300)):
ih, iw, _ = image.shape
h, w = image_size
if not is_training:
return _infer_data(image, image_size)
# Random crop
box = box.astype(np.float32)
image, box = random_sample_crop(image, box)
ih, iw, _ = image.shape
# Resize image
image = cv2.resize(image, (w, h))
# Flip image or not
flip = _rand() < .5
if flip:
image = cv2.flip(image, 1, dst=None)
# When the channels of image is 1
if len(image.shape) == 2:
image = np.expand_dims(image, axis=-1)
image = np.concatenate([image, image, image], axis=-1)
box[:, [0, 2]] = box[:, [0, 2]] / ih
box[:, [1, 3]] = box[:, [1, 3]] / iw
if flip:
box[:, [1, 3]] = 1 - box[:, [3, 1]]
box, label, num_match = ssd_bboxes_encode(box)
return image, box, label, num_match
return _data_aug(image, box, is_training, image_size=config.img_shape)
数据集创建
import multiprocessing
import mindspore.dataset as de
def create_ssd_dataset(mindrecord_file, batch_size=32, device_num=1, rank=0,
is_training=True, num_parallel_workers=1, use_multiprocessing=True):
"""Create SSD dataset with MindDataset."""
ds = de.MindDataset(mindrecord_file, columns_list=["img_id", "image", "annotation"], num_shards=device_num,
shard_id=rank, num_parallel_workers=num_parallel_workers, shuffle=is_training)
decode = de.vision.Decode()
ds = ds.map(operations=decode, input_columns=["image"])
change_swap_op = de.vision.HWC2CHW()
# Computed from random subset of ImageNet training images
normalize_op = de.vision.Normalize(mean=[0.485 * 255, 0.456 * 255, 0.406 * 255],
std=[0.229 * 255, 0.224 * 255, 0.225 * 255])
color_adjust_op = de.vision.RandomColorAdjust(brightness=0.4, contrast=0.4, saturation=0.4)
compose_map_func = (lambda img_id, image, annotation: preprocess_fn(img_id, image, annotation, is_training))
if is_training:
output_columns = ["image", "box", "label", "num_match"]
trans = [color_adjust_op, normalize_op, change_swap_op]
else:
output_columns = ["img_id", "image", "image_shape"]
trans = [normalize_op, change_swap_op]
ds = ds.map(operations=compose_map_func, input_columns=["img_id", "image", "annotation"],
output_columns=output_columns, column_order=output_columns,
python_multiprocessing=use_multiprocessing,
num_parallel_workers=num_parallel_workers)
ds = ds.map(operations=trans, input_columns=["image"], python_multiprocessing=use_multiprocessing,
num_parallel_workers=num_parallel_workers)
ds = ds.batch(batch_size, drop_remainder=True)
return ds
2.2 模型构建
2.2 模型构建
SSD的网络结构主要分为以下几个部分:
- VGG16 Base Layer
- Extra Feature Layer
- Detection Layer
- NMS
- Anchor
Backbone Layer
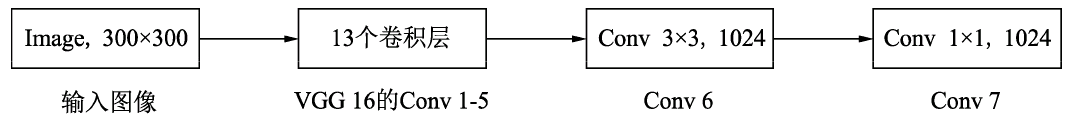
输入图像经过预处理后大小固定为300×300,首先经过backbone,本案例中使用的是VGG16网络的前13个卷积层,然后分别将VGG16的全连接层fc6和fc7转换成3$\times$3卷积层block6和1$\times$1卷积层block7,进一步提取特征。 在block6中,使用了空洞数为6的空洞卷积,其padding也为6,这样做同样也是为了增加感受野的同时保持参数量与特征图尺寸的不变。
Extra Feature Layer
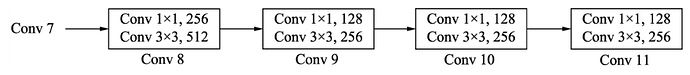
在VGG16的基础上,SSD进一步增加了4个深度卷积层,用于提取更高层的语义信息:
block8-11,用于更高语义信息的提取。block8的通道数为512,而block9、block10与block11的通道数都为256。从block7到block11,这5个卷积后输出特征图的尺寸依次为19×19、10×10、5×5、3×3和1×1。为了降低参数量,使用了1×1卷积先降低通道数为该层输出通道数的一半,再利用3×3卷积进行特征提取。
Anchor
SSD采用了PriorBox来进行区域生成。将固定大小宽高的PriorBox作为先验的感兴趣区域,利用一个阶段完成能够分类与回归。设计大量的密集的PriorBox保证了对整幅图像的每个地方都有一一的检测。PriorBox位置的表示形式是以中心点坐标和框的宽、高(cx,cy,w,h)来表示的,同时都转换成百分比的形式。
PriorBox生成规则:
SSD由6个特征层来检测目标,在不同特征层上,PriorBox的尺寸scale大小是不一样的,最低层的scale=0.1,最高层的scale=0.95,其他层的计算公式如下:
在某个特征层上其scale一定,那么会设置不同长宽比ratio的PriorBox,其长和宽的计算公式如下:
在ratio=1的时候,还会根据该特征层和下一个特征层计算一个特定scale的PriorBox(长宽比ratio=1),计算公式如下:
每个特征层的每个点都会以上述规则生成PriorBox,(cx,cy)由当前点的中心点来确定,由此每个特征层都生成大量密集的PriorBox,如下图:
SSD使用了第4、7、8、9、10和11这6个卷积层得到的特征图,这6个特征图尺寸越来越小,而其对应的感受野越来越大。6个特征图上的每一个点分别对应4、6、6、6、4、4个PriorBox。某个特征图上的一个点根据下采样率可以得到在原图的坐标,以该坐标为中心生成4个或6个不同大小的PriorBox,然后利用特征图的特征去预测每一个PriorBox对应类别与位置的预测量。例如:第8个卷积层得到的特征图大小为10×10×512,每个点对应6个PriorBox,一共有600个PriorBox。定义MultiBox类,生成多个预测框。
Detection Layer
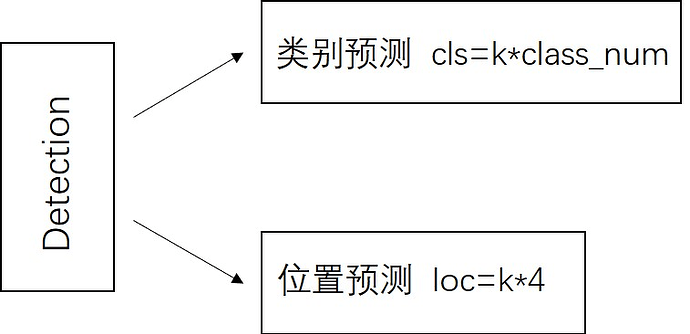
SSD模型一共有6个预测特征图,对于其中一个尺寸为m*n,通道为p的预测特征图,假设其每个像素点会产生k个anchor,每个anchor会对应c个类别和4个回归偏移量,使用(4+c)k个尺寸为3x3,通道为p的卷积核对该预测特征图进行卷积操作,得到尺寸为m*n,通道为(4+c)m*k的输出特征图,它包含了预测特征图上所产生的每个anchor的回归偏移量和各类别概率分数。所以对于尺寸为m*n的预测特征图,总共会产生(4+c)k*m*n个结果。cls分支的输出通道数为k*class_num,loc分支的输出通道数为k*4。
import mindspore as ms
import mindspore.nn as nn
from src.vgg16 import vgg16
import mindspore.ops as ops
import ml_collections
from src.config import get_config
config = get_config()
def _make_divisible(v, divisor, min_value=None):
"""ensures that all layers have a channel number that is divisible by 8."""
if min_value is None:
min_value = divisor
new_v = max(min_value, int(v + divisor / 2) // divisor * divisor)
# Make sure that round down does not go down by more than 10%.
if new_v < 0.9 * v:
new_v += divisor
return new_v
def _conv2d(in_channel, out_channel, kernel_size=3, stride=1, pad_mod='same'):
return nn.Conv2d(in_channel, out_channel, kernel_size=kernel_size, stride=stride,
padding=0, pad_mode=pad_mod, has_bias=True)
def _bn(channel):
return nn.BatchNorm2d(channel, eps=1e-3, momentum=0.97,
gamma_init=1, beta_init=0, moving_mean_init=0, moving_var_init=1)
def _last_conv2d(in_channel, out_channel, kernel_size=3, stride=1, pad_mod='same', pad=0):
in_channels = in_channel
out_channels = in_channel
depthwise_conv = nn.Conv2d(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size, stride, pad_mode='same',
padding=pad, group=in_channels)
conv = _conv2d(in_channel, out_channel, kernel_size=1)
return nn.SequentialCell([depthwise_conv, _bn(in_channel), nn.ReLU6(), conv])
class FlattenConcat(nn.Cell):
def __init__(self, config):
super(FlattenConcat, self).__init__()
self.num_ssd_boxes = config.num_ssd_boxes
self.concat = ops.Concat(axis=1)
self.transpose = ops.Transpose()
def construct(self, inputs):
output = ()
batch_size = ops.shape(inputs[0])[0]
for x in inputs:
x = self.transpose(x, (0, 2, 3, 1))
output += (ops.reshape(x, (batch_size, -1)),)
res = self.concat(output)
return ops.reshape(res, (batch_size, self.num_ssd_boxes, -1))
class GridAnchorGenerator:
"""
Anchor Generator
"""
def __init__(self, image_shape, scale, scales_per_octave, aspect_ratios):
super(GridAnchorGenerator, self).__init__()
self.scale = scale
self.scales_per_octave = scales_per_octave
self.aspect_ratios = aspect_ratios
self.image_shape = image_shape
def generate(self, step):
scales = np.array([2**(float(scale) / self.scales_per_octave)
for scale in range(self.scales_per_octave)]).astype(np.float32)
aspects = np.array(list(self.aspect_ratios)).astype(np.float32)
scales_grid, aspect_ratios_grid = np.meshgrid(scales, aspects)
scales_grid = scales_grid.reshape([-1])
aspect_ratios_grid = aspect_ratios_grid.reshape([-1])
feature_size = [self.image_shape[0] / step, self.image_shape[1] / step]
grid_height, grid_width = feature_size
base_size = np.array([self.scale * step, self.scale * step]).astype(np.float32)
anchor_offset = step / 2.0
ratio_sqrt = np.sqrt(aspect_ratios_grid)
heights = scales_grid / ratio_sqrt * base_size[0]
widths = scales_grid * ratio_sqrt * base_size[1]
y_centers = np.arange(grid_height).astype(np.float32)
y_centers = y_centers * step + anchor_offset
x_centers = np.arange(grid_width).astype(np.float32)
x_centers = x_centers * step + anchor_offset
x_centers, y_centers = np.meshgrid(x_centers, y_centers)
x_centers_shape = x_centers.shape
y_centers_shape = y_centers.shape
widths_grid, x_centers_grid = np.meshgrid(widths, x_centers.reshape([-1]))
heights_grid, y_centers_grid = np.meshgrid(heights, y_centers.reshape([-1]))
x_centers_grid = x_centers_grid.reshape(*x_centers_shape, -1)
y_centers_grid = y_centers_grid.reshape(*y_centers_shape, -1)
widths_grid = widths_grid.reshape(-1, *x_centers_shape)
heights_grid = heights_grid.reshape(-1, *y_centers_shape)
bbox_centers = np.stack([y_centers_grid, x_centers_grid], axis=3)
bbox_sizes = np.stack([heights_grid, widths_grid], axis=3)
bbox_centers = bbox_centers.reshape([-1, 2])
bbox_sizes = bbox_sizes.reshape([-1, 2])
bbox_corners = np.concatenate([bbox_centers - 0.5 * bbox_sizes, bbox_centers + 0.5 * bbox_sizes], axis=1)
self.bbox_corners = bbox_corners / np.array([*self.image_shape, *self.image_shape]).astype(np.float32)
self.bbox_centers = np.concatenate([bbox_centers, bbox_sizes], axis=1)
self.bbox_centers = self.bbox_centers / np.array([*self.image_shape, *self.image_shape]).astype(np.float32)
print(self.bbox_centers.shape)
return self.bbox_centers, self.bbox_corners
def generate_multi_levels(self, steps):
bbox_centers_list = []
bbox_corners_list = []
for step in steps:
bbox_centers, bbox_corners = self.generate(step)
bbox_centers_list.append(bbox_centers)
bbox_corners_list.append(bbox_corners)
self.bbox_centers = np.concatenate(bbox_centers_list, axis=0)
self.bbox_corners = np.concatenate(bbox_corners_list, axis=0)
return self.bbox_centers, self.bbox_corners
class MultiBox(nn.Cell):
"""
Multibox conv layers. Each multibox layer contains class conf scores and localization predictions.
"""
def __init__(self, config):
super(MultiBox, self).__init__()
num_classes = 81
out_channels = [512, 1024, 512, 256, 256, 256]
num_default = config.num_default
loc_layers = []
cls_layers = []
for k, out_channel in enumerate(out_channels):
loc_layers += [_last_conv2d(out_channel, 4 * num_default[k],
kernel_size=3, stride=1, pad_mod='same', pad=0)]
cls_layers += [_last_conv2d(out_channel, num_classes * num_default[k],
kernel_size=3, stride=1, pad_mod='same', pad=0)]
self.multi_loc_layers = nn.layer.CellList(loc_layers)
self.multi_cls_layers = nn.layer.CellList(cls_layers)
self.flatten_concat = FlattenConcat(config)
def construct(self, inputs):
loc_outputs = ()
cls_outputs = ()
for i in range(len(self.multi_loc_layers)):
loc_outputs += (self.multi_loc_layers[i](inputs[i]),)
cls_outputs += (self.multi_cls_layers[i](inputs[i]),)
return self.flatten_concat(loc_outputs), self.flatten_concat(cls_outputs)
class SSD300VGG16(nn.Cell):
def __init__(self, config):
super(SSD300VGG16, self).__init__()
# VGG16 backbone: block1~5
self.backbone = vgg16()
# SSD blocks: block6~7
self.b6_1 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=512, out_channels=1024, kernel_size=3, padding=6, dilation=6, pad_mode='pad')
self.b6_2 = nn.Dropout(0.5)
self.b7_1 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=1024, out_channels=1024, kernel_size=1)
self.b7_2 = nn.Dropout(0.5)
# Extra Feature Layers: block8~11
self.b8_1 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=1024, out_channels=256, kernel_size=1, padding=1, pad_mode='pad')
self.b8_2 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=256, out_channels=512, kernel_size=3, stride=2, pad_mode='valid')
self.b9_1 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=512, out_channels=128, kernel_size=1, padding=1, pad_mode='pad')
self.b9_2 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=128, out_channels=256, kernel_size=3, stride=2, pad_mode='valid')
self.b10_1 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=256, out_channels=128, kernel_size=1)
self.b10_2 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=128, out_channels=256, kernel_size=3, pad_mode='valid')
self.b11_1 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=256, out_channels=128, kernel_size=1)
self.b11_2 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=128, out_channels=256, kernel_size=3, pad_mode='valid')
# boxes
self.multi_box = MultiBox(config)
if not self.training:
self.activation = ops.Sigmoid()
def construct(self, x):
# VGG16 backbone: block1~5
block4, x = self.backbone(x)
# SSD blocks: block6~7
x = self.b6_1(x) # 1024
x = self.b6_2(x)
x = self.b7_1(x) # 1024
x = self.b7_2(x)
block7 = x
# Extra Feature Layers: block8~11
x = self.b8_1(x) # 256
x = self.b8_2(x) # 512
block8 = x
x = self.b9_1(x) # 128
x = self.b9_2(x) # 256
block9 = x
x = self.b10_1(x) # 128
x = self.b10_2(x) # 256
block10 = x
x = self.b11_1(x) # 128
x = self.b11_2(x) # 256
block11 = x
# boxes
multi_feature = (block4, block7, block8, block9, block10, block11)
pred_loc, pred_label = self.multi_box(multi_feature)
if not self.training:
pred_label = self.activation(pred_label)
pred_loc = ops.cast(pred_loc, ms.float32)
pred_label = ops.cast(pred_label, ms.float32)
return pred_loc, pred_label
def ssd_vgg16(**kwargs):
return SSD300VGG16(**kwargs)