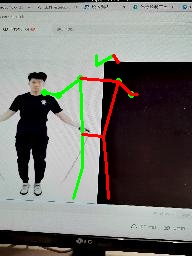
我将我的rtmpose的onnx模型分别转为tflite和鸿蒙时,推理结果不一致,
tflite推理结果:
鸿蒙模型推理结果:
鸿蒙模型推理的点总数位于屏幕中间,由于模型输入是全图,虽然tflite推理结果乱一点,但大体是在人体附近的
tflite推理代码:
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
import time
import cv2
from typing import List, Tuple
from onnx_predict import visualize
def get_simcc_maximum(simcc_x: np.ndarray,
simcc_y: np.ndarray) → Tuple[np.ndarray, np.ndarray]:
“”"Get maximum response location and value from simcc representations.
Note:
instance number: N
num_keypoints: K
heatmap height: H
heatmap width: W
Args:
simcc_x (np.ndarray): x-axis SimCC in shape (K, Wx) or (N, K, Wx)
simcc_y (np.ndarray): y-axis SimCC in shape (K, Wy) or (N, K, Wy)
Returns:
tuple:
- locs (np.ndarray): locations of maximum heatmap responses in shape
(K, 2) or (N, K, 2)
- vals (np.ndarray): values of maximum heatmap responses in shape
(K,) or (N, K)
"""
N, K, Wx = simcc_x.shape
simcc_x = simcc_x.reshape(N * K, -1)
simcc_y = simcc_y.reshape(N * K, -1)
# get maximum value locations
x_locs = np.argmax(simcc_x, axis=1) # 返回索引值
y_locs = np.argmax(simcc_y, axis=1)
locs = np.stack((x_locs, y_locs), axis=-1).astype(np.float32)
max_val_x = np.amax(simcc_x, axis=1) # 返回值,axis是列
max_val_y = np.amax(simcc_y, axis=1)
# get maximum value across x and y axis
mask = max_val_x > max_val_y # 点的置信度
max_val_x[mask] = max_val_y[mask]
vals = max_val_x
locs[vals <= 0.] = -1
# reshape
locs = locs.reshape(N, K, 2)
vals = vals.reshape(N, K)
return locs, vals
def decode(simcc_x: np.ndarray, simcc_y: np.ndarray,
simcc_split_ratio) → Tuple[np.ndarray, np.ndarray]:
“”"Modulate simcc distribution with Gaussian.
Args:
simcc_x (np.ndarray[K, Wx]): model predicted simcc in x.
simcc_y (np.ndarray[K, Wy]): model predicted simcc in y.
simcc_split_ratio (int): The split ratio of simcc.
Returns:
tuple: A tuple containing center and scale.
- np.ndarray[float32]: keypoints in shape (K, 2) or (n, K, 2)
- np.ndarray[float32]: scores in shape (K,) or (n, K)
"""
keypoints, scores = get_simcc_maximum(simcc_x, simcc_y)
keypoints /= simcc_split_ratio
return keypoints, scores
def postprocess(outputs: List[np.ndarray],
simcc_split_ratio: float = 2.0
) → Tuple[np.ndarray, np.ndarray]:
“”"Postprocess for RTMPose model output.
Args:
outputs (np.ndarray): Output of RTMPose model.
model_input_size (tuple): RTMPose model Input image size.
center (tuple): Center of bbox in shape (x, y).
scale (tuple): Scale of bbox in shape (w, h).
simcc_split_ratio (float): Split ratio of simcc.
Returns:
tuple:
- keypoints (np.ndarray): Rescaled keypoints.
- scores (np.ndarray): Model predict scores.
"""
# use simcc to decode
# print(outputs.outputs.shape())
# print()
simcc_x, simcc_y = outputs[0][:, :384, :], outputs[0][:, 384:, :]
simcc_x = np.transpose(simcc_x, (0, 2, 1))
simcc_y = np.transpose(simcc_y, (0, 2, 1))
keypoints, scores = decode(simcc_x, simcc_y, simcc_split_ratio)
return keypoints, scores
def tflite_inf(input_test_tflite_file1, input_test_tflite_file2, input_image_path, vis_image_path):
img = cv2.imread(input_image_path)
# new_img, center, scale = preprocess(img, (192, 256)) # 2561923
# new_img = np.random.uniform(0, 1, (1, 256, 192, 3))
new_img = np.expand_dims(img, axis=0) # 1256192*3
new_img = new_img.astype(np.float32) # 类型也要满足要求
print(“-----------------------------”)
# init model1
interpreter1 = tf.lite.Interpreter(model_path=input_test_tflite_file1)
tensor_details1 = interpreter1.get_tensor_details()
for i in range(0, len(tensor_details1)):
print(“tensor1:”, i, tensor_details1[i])
interpreter1.allocate_tensors()
input_details1 = interpreter1.get_input_details()
print(“=======================================”)
print(“input1:”, str(input_details1))
output_details1 = interpreter1.get_output_details()
print(“ouput1:”, str(output_details1))
print(“=======================================”)
# init model2
interpreter2 = tf.lite.Interpreter(model_path=input_test_tflite_file2)
tensor_details2 = interpreter2.get_tensor_details()
for i in range(0, len(tensor_details2)):
print(“tensor2:”, i, tensor_details2[i])
interpreter2.allocate_tensors()
input_details2 = interpreter2.get_input_details()
print(“=======================================”)
print(“input2 :”, str(input_details2))
output_details2 = interpreter2.get_output_details()
print(“ouput2 :”, str(output_details2))
print(“=======================================”)
interpreter1.set_tensor(input_details1[0]['index'], new_img)
t1 = time.time()
interpreter1.invoke()
print("time cost : ", time.time() - t1)
output_data1 = interpreter1.get_tensor(output_details1[0]['index'])
print("output_data1",output_data1.shape) # 1*8*6*21
# reshape
new_img2 = np.transpose(np.transpose(output_data1, axes=(0, 3, 1, 2)).reshape(1, 21, 48), axes=(0, 2, 1))
# new_img2 = np.transpose(np.transpose(output_data1, axes=(0, 3, 1, 2)).reshape(1, 17, 48), axes=(0, 2, 1))
print(new_img2.shape) # 1*48*21
print("input_details1[0]['index']:",input_details1[0]['index'])
interpreter2.set_tensor(input_details1[0]['index'], new_img2)
t2 = time.time()
interpreter2.invoke()
print("time cost : ", time.time() - t2)
output_data2 = interpreter2.get_tensor(output_details2[0]['index'])
print("test_tflite finish!")
# output_data2 = [np.transpose(output_data2, axes=(0, 2, 1))]
output_data2 = [output_data2]
print("output_data2", output_data2[0].shape) # 1*896*21
keypoints, scores = postprocess(output_data2)
visualize(img, keypoints, scores, vis_image_path)
if name == ‘main’:
intput_tflite_file1 = “/media/disk1/pose_estimation/codes/RTMPose/work_dirs/20250519_app_stand_trc_add_raise-data/250522_trc_stage1.tflite”
# intput_tflite_file1 = “/media/disk1/pose_estimation/codes/RTMPose/work_dirs/20250311_app_stand_t/0311_stage1.tflite”
intput_tflite_file2 = “/media/disk1/pose_estimation/codes/RTMPose/work_dirs/20250519_app_stand_trc_add_raise-data/250522_trc_stage2.tflite”
# intput_tflite_file2 = “/media/disk1/pose_estimation/codes/RTMPose/work_dirs/20250311_app_stand_t/0311_stage2.tflite”
# input_image_path = “/media/disk1/pose_estimation/codes/RTMPose/projects/rtmpose/examples/onnxruntime/human-pose1.jpeg”
input_image_path = “/media/disk1/pose_estimation/codes/RTMPose/work_dirs/app_test_stand_image/5.jpg”
vis_image_path = “/media/disk1/pose_estimation/codes/RTMPose/work_dirs/20250519_app_stand_trc_add_raise-data/res5.jpg”
tflite_inf(intput_tflite_file1, intput_tflite_file2, input_image_path, vis_image_path)
鸿蒙推理参考的是:
代码如下:
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include <opencv2/opencv.hpp>
#include “include/api/model.h”
#include “include/api/context.h”
#include “include/api/status.h”
#include “include/api/types.h”
using mindspore::MSTensor;
// 读取二进制文件
char *ReadFile(const char *file, size_t *size) {
if (file == nullptr) {
std::cerr << “file is nullptr.” << std::endl;
return nullptr;
}
std::ifstream ifs(file, std::ifstream::in | std::ifstream::binary);
if (!ifs.good()) {
std::cerr << “file: " << file << " is not exist.” << std::endl;
return nullptr;
}
if (!ifs.is_open()) {
std::cerr << “file: " << file << " open failed.” << std::endl;
return nullptr;
}
ifs.seekg(0, std::ios::end);
*size = ifs.tellg();
std::unique_ptr<char> buf(new (std::nothrow) char[*size]);
if (buf == nullptr) {
std::cerr << "malloc buf failed, file: " << file << std::endl;
ifs.close();
return nullptr;
}
ifs.seekg(0, std::ios::beg);
ifs.read(buf.get(), *size);
ifs.close();
return buf.release();
}
// 保存推理结果到文件
void SaveOutput(const std::string &filename, float *data, size_t num) {
std::ofstream ofs(filename, std::ios::binary);
ofs.write(reinterpret_cast<const char *>(data), num * sizeof(float));
ofs.close();
}
// 打印shape
void PrintShape(const std::vector<int64_t>& shape, const std::string& name) {
std::cout << name << " shape: [";
for (size_t i = 0; i < shape.size(); ++i) {
std::cout << shape[i];
if (i != shape.size() - 1) std::cout << ", ";
}
std::cout << “]” << std::endl;
}
int main(int argc, const char **argv) {
std::string img_path = “../test_img/4.jpg”;
std::string stage1_path = “../model/stage1_0311_inline_float16.ms”;
std::string stage2_path = “../model/stage2_0311_inline_float16.ms”;
// std::string stage1_path = “../model/20250519_app_trc_stage1_online.ms”;
// std::string stage2_path = “../model/20250519_app_trc_stage2_online.ms”;
std::string out_path = “../test_img/output_stage2.bin”;
std::string vis_path = “../test_img/vis_result4_0311_float16.jpg”;
// 读取图片并预处理
cv::Mat img = cv::imread(img_path);
if (img.empty()) {
std::cerr << "Read image failed: " << img_path << std::endl;
return -1;
}
// 直接resize到(256,192),float32归一化
cv::Mat img_resized;
cv::resize(img, img_resized, cv::Size(192, 256));
img_resized.convertTo(img_resized, CV_32FC3);
cv::cvtColor(img_resized, img_resized, cv::COLOR_BGR2RGB);
// 归一化:减均值除以方差
cv::Scalar mean(123.675f, 116.28f, 103.53f);
cv::Scalar std(58.395f, 57.12f, 57.375f);
cv::Mat img_norm;
cv::subtract(img_resized, mean, img_norm);
cv::divide(img_norm, std, img_norm);
// 按NHWC顺序存储
std::vector input_img;
input_img.assign((float*)img_norm.datastart, (float*)img_norm.dataend);
std::cout << “Stage1 input shape: [1, 256, 192, 3]” << std::endl;
// 加载stage1模型
size_t size1 = 0;
char *model_buf1 = ReadFile(stage1_path.c_str(), &size1);
if (!model_buf1) { std::cerr << “Read stage1 model failed\n”; return -1; }
auto context = std::make_sharedmindspore::Context();
context->MutableDeviceInfo().push_back(std::make_sharedmindspore::CPUDeviceInfo());
auto model1 = new mindspore::Model();
if (model1->Build(model_buf1, size1, mindspore::kMindIR, context) != mindspore::kSuccess) {
std::cerr << “Build stage1 model error\n”; delete model_buf1; delete model1; return -1;
}
delete model_buf1;
// 设置stage1输入
auto inputs1 = model1->GetInputs();
if (inputs1.empty()) { std::cerr << “Stage1 input empty\n”; delete model1; return -1; }
auto &tensor1 = inputs1[0];
memcpy(tensor1.MutableData(), input_img.data(), input_img.size() * sizeof(float));
// 推理stage1
std::vector outputs1;
if (model1->Predict(inputs1, &outputs1) != mindspore::kSuccess) {
std::cerr << “Stage1 inference error\n”; delete model1; return -1;
}
// 输出shape为(1, 21, 8, 6)
std::vector<int64_t> out1_shape = outputs1[0].Shape();
PrintShape(out1_shape, “Stage1 output”);
if (out1_shape.size() != 4 || out1_shape[1] != 21 || out1_shape[2] != 8 || out1_shape[3] != 6) {
std::cerr << “Unexpected stage1 output shape!” << std::endl;
delete model1;
return -1;
}
float *out1_data = reinterpret_cast<float *>(outputs1[0].MutableData());
// (1, 21, 8, 6) → (1, 21, 48)
int N = static_cast(out1_shape[0]);
int K = static_cast(out1_shape[1]);
int H = static_cast(out1_shape[2]);
int W = static_cast(out1_shape[3]);
std::vector stage2_input(N * K * H * W);
for (int n = 0; n < N; ++n)
for (int k = 0; k < K; ++k)
for (int h = 0; h < H; ++h)
for (int w = 0; w < W; ++w)
stage2_input[n * (K * H * W) + k * (H * W) + h * W + w] =
out1_data[n * (K * H * W) + k * (H * W) + h * W + w];
std::cout << “Stage2 input shape: [1, 21, 48]” << std::endl;
delete model1;
// 加载stage2模型
size_t size2 = 0;
char *model_buf2 = ReadFile(stage2_path.c_str(), &size2);
if (!model_buf2) { std::cerr << “Read stage2 model failed\n”; return -1; }
auto model2 = new mindspore::Model();
if (model2->Build(model_buf2, size2, mindspore::kMindIR, context) != mindspore::kSuccess) {
std::cerr << “Build stage2 model error\n”; delete model_buf2; delete model2; return -1;
}
delete model_buf2;
// 设置stage2输入
auto inputs2 = model2->GetInputs();
if (inputs2.empty()) { std::cerr << “Stage2 input empty\n”; delete model2; return -1; }
auto &tensor2 = inputs2[0];
memcpy(tensor2.MutableData(), stage2_input.data(), stage2_input.size() * sizeof(float));
// 推理stage2
std::vector outputs2;
if (model2->Predict(inputs2, &outputs2) != mindspore::kSuccess) {
std::cerr << “Stage2 inference error\n”; delete model2; return -1;
}
// 输出shape为(1, 896, 21)
std::vector<int64_t> out2_shape = outputs2[0].Shape();
PrintShape(out2_shape, “Stage2 output”);
float *out2_data = reinterpret_cast<float *>(outputs2[0].MutableData());
size_t out2_num = outputs2[0].ElementNum();
SaveOutput(out_path, out2_data, out2_num);
std::cout << "Stage2 output saved to: " << out_path << std::endl;
// ----------- 后处理与可视化 -----------
int N2 = out2_shape[0];
int HW = out2_shape[1]; // 896
int K2 = out2_shape[2]; // 21
int Wx = 384, Wy = 512;
float simcc_split_ratio = 2.0f;
// 拆分simcc_x和simcc_y
std::vector<std::vectorcv::Point2f> keypoints(N2, std::vectorcv::Point2f(K2));
std::vector<std::vector> scores(N2, std::vector(K2));
for (int n = 0; n < N2; ++n) {
// simcc_x: (K, Wx), simcc_y: (K, Wy)
for (int k = 0; k < K2; ++k) {
// x
int x_offset = n * HW * K2 + 0;
float max_x = -1e10f;
int max_x_idx = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < Wx; ++i) {
float v = out2_data[n * HW * K2 + i * K2 + k];
if (v > max_x) { max_x = v; max_x_idx = i; }
}
// y
float max_y = -1e10f;
int max_y_idx = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < Wy; ++i) {
float v = out2_data[n * HW * K2 + (i + Wx) * K2 + k];
if (v > max_y) { max_y = v; max_y_idx = i; }
}
// 得分取较小值
float conf = std::min(max_x, max_y);
if (conf <= 0) {
keypoints[n][k] = cv::Point2f(-1, -1);
scores[n][k] = 0;
} else {
keypoints[n][k] = cv::Point2f(max_x_idx / simcc_split_ratio, max_y_idx / simcc_split_ratio);
scores[n][k] = conf;
}
}
}
// 可视化
cv::Mat vis_img = img.clone();
// 画关键点
for (int k = 0; k < K2; ++k) {
if (scores[0][k] > 0.2f) {
cv::circle(vis_img, keypoints[0][k], 2, cv::Scalar(0, 255, 0), 2);
}
}
// 画连接线
int connections[16][2] = {
{0, 1}, {0, 2}, {1, 3}, {2, 4}, {5, 7}, {6, 8}, {7, 9}, {8, 10},
{11, 13}, {12, 14}, {13, 15}, {14, 16}, {5, 11}, {6, 12}, {11, 12}, {5, 6}
};
for (int i = 0; i < 16; ++i) {
int kp1 = connections[i][0];
int kp2 = connections[i][1];
if (scores[0][kp1] > 0.1f && scores[0][kp2] > 0.1f) {
cv::Scalar color;
if (kp1 % 2 == 0)
color = cv::Scalar(0, 255, 0); // 偶数绿色
else
color = cv::Scalar(0, 0, 255); // 奇数红色
cv::line(vis_img, keypoints[0][kp1], keypoints[0][kp2], color, 2);
}
}
cv::imwrite(vis_path, vis_img);
std::cout << "Visualized result saved to: " << vis_path << std::endl;
delete model2;
return 0;
}